Human brain
The human brain is a complex organ that serves as the control center of the central nervous system in humans. It is responsible for processing information, coordinating bodily functions, and enabling conscious thought and awareness.
Here are some key facts about the human brain:
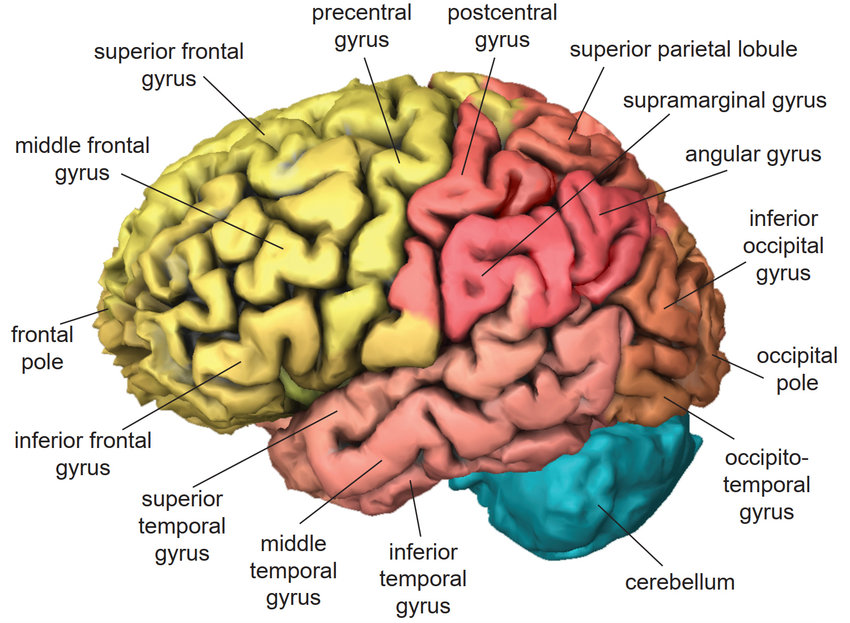
1. Structure: The brain is located within the skull and weighs about 1.4 kilograms (3 pounds) on average. It has a wrinkled appearance due to the presence of folds and grooves called gyri and sulci, respectively. The brain is divided into several major regions, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
2.Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for higher cognitive functions, such as perception, memory, language, and decision-making. It is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, which are connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum.
3.Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain, beneath the cerebrum. It plays a crucial role in coordinating voluntary movements, balance, and posture.
4.Brainstem: The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord. It regulates basic functions necessary for survival, including breathing, heart rate, and digestion. It also serves as a relay station, transmitting information between the brain and the rest of the body.
5.Neurons: Neurons are the basic building blocks of the brain. They are specialized cells that transmit electrical signals and enable communication within the nervous system. The brain contains billions of neurons, which form intricate networks and pathways.
6.Synapses: Neurons communicate with each other through junctions called synapses. These synapses allow electrical or chemical signals to pass from one neuron to another, facilitating the transmission of information.
7.Plasticity: The brain exhibits a remarkable ability to change and adapt, known as neuroplasticity. It can reorganize its structure and function in response to learning, experience, and injury. This plasticity is the basis for learning and memory formation.
8.Consciousness: The brain is closely associated with consciousness—the subjective experience of being aware and perceiving the world. The mechanisms underlying consciousness are still not fully understood and remain a topic of scientific investigation.
9.Disorders and Diseases: Various disorders and diseases can affect the brain, including neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, mental health disorders like depression and schizophrenia, and traumatic brain injuries.
10.Studying the human brain is a multidisciplinary field that encompasses neuroscience, psychology, and other related disciplines. Scientists continue to explore the complexities of the brain to deepen our understanding of its functions and develop treatments for brain-related disorders.