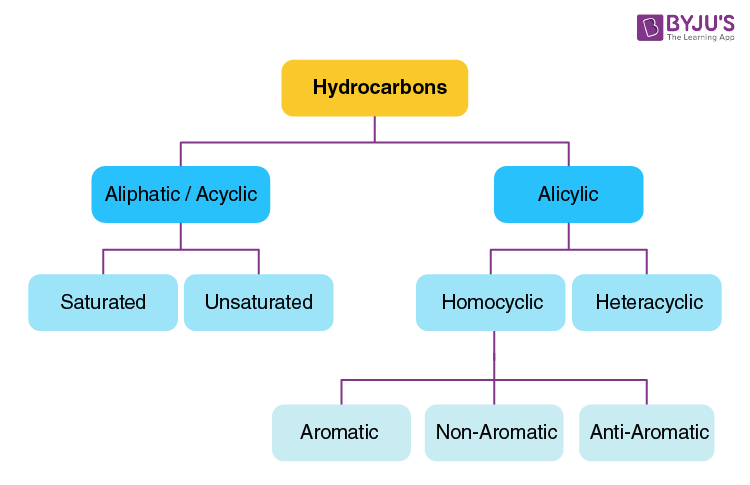
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are the fundamental building blocks of many organic substances, including fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Hydrocarbons are characterized by their carbon ske

There are different types of hydrocarbons, classified based on the arrangement of carbon atoms and the types of bonds between them. Here are a few common categories:
Alkanes: Also known as paraffins, alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with single bonds between carbon atoms. Methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and butane (C4H10) are examples of alkanes.
Alkenes: These are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Ethene (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are examples of alkenes.
Alkynes: Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that feature at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. Ethyne (C2H2) is an example of an alkyne.
Aromatic hydrocarbons: Aromatic compounds have a unique ring structure called a benzene ring. Benzene (C6H6) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon, and it is known for its distinct aroma.
Hydrocarbons have various uses and applications. Fossil fuels derived from hydrocarbons, such as petroleum and natural gas, are vital energy sources for transportation, heating, and electricity generation. Hydrocarbons are also used as raw materials in the production of plastics, solvents, lubricants, waxes, and many other chemicals.
However, it is worth noting that the combustion of hydrocarbons contributes to air pollution and the emission of greenhouse gases, which are associated with climate change. As the world seeks to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and transition to more sustainable energy sources, the development and utilization of alternative energy technologies are becoming increasingly important.