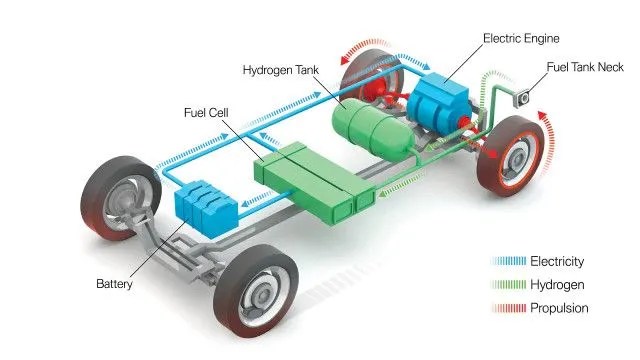
A hydrogen engine, also known as a hydrogen internal combustion engine (HICE), is an engine that burns hydrogen as its fuel source to generate power. Similar to traditional internal combustion engines, hydrogen engines use a combustion process to convert the chemical energy in hydrogen into mechanical energy.
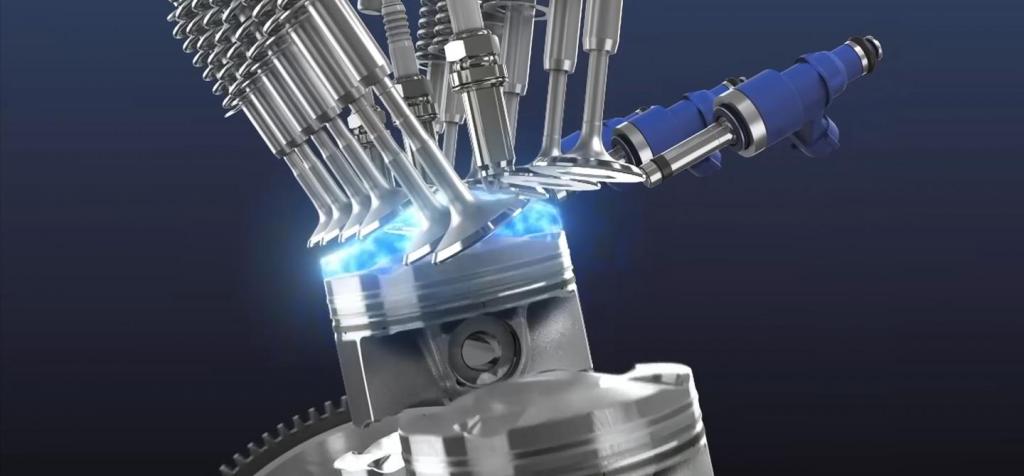

A hydrogen engine is an internal combustion engine (ICE) that operates on hydrogen as a fuel source. It is designed to convert the chemical energy stored in hydrogen gas into mechanical energy, which can be used to power vehicles, machinery, or generators.
Unlike traditional internal combustion engines that use gasoline or diesel fuel, hydrogen engines burn hydrogen as the primary fuel. When hydrogen combines with oxygen in the engine’s combustion chamber, it undergoes a chemical reaction known as combustion, resulting in the production of water vapor and the release of energy. This process is often referred to as hydrogen combustion.
Hydrogen engines can be classified into two main types:
Spark Ignition (SI) Engines: These engines operate similarly to gasoline engines. Hydrogen is mixed with air, and a spark plug ignites the hydrogen-air mixture, causing combustion. The energy released from combustion drives the engine’s pistons, which generates mechanical power.
Compression Ignition (CI) Engines: These engines operate similarly to diesel engines. Hydrogen is injected into the combustion chamber, where it is compressed by the piston. The high temperature and pressure cause the hydrogen to self-ignite, leading to combustion. The resulting expansion of gases drives the piston and generates power.
Advantages of Hydrogen Engines:
1.Zero Emissions: The primary advantage of hydrogen engines is that they produce zero harmful emissions when hydrogen is burned. The only byproduct of hydrogen combustion is water vapor, making it a clean and environmentally friendly fuel option.
2.High Energy Efficiency: Hydrogen has a high energy-to-weight ratio, making it an efficient fuel source. Hydrogen engines can achieve high thermal efficiencies, which means they can convert a large portion of the energy contained in hydrogen into useful mechanical work.
3.Renewable Energy Compatibility: Hydrogen can be produced using various methods, including electrolysis, which can be powered by renewable energy sources like wind or solar. This makes hydrogen engines a potential solution for utilizing renewable energy in transportation and other sectors.
Challenges and Limitations:
1.Hydrogen Infrastructure: The widespread adoption of hydrogen engines faces challenges related to infrastructure development. Building a comprehensive hydrogen refueling network is required to support the refueling needs of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
2.Fuel Storage and Safety: Hydrogen has low energy density compared to gasoline or diesel, which means it requires larger storage tanks. Safety concerns regarding hydrogen storage and handling, such as potential leaks or explosions, need to be addressed and mitigated.
3.Production Challenges: The production of hydrogen often relies on fossil fuels, such as natural gas, which can result in carbon emissions. Scaling up the production of hydrogen from renewable sources is necessary to minimize environmental impact.
4.Cost: Currently, the production and storage of hydrogen are relatively expensive compared to conventional fuels. However, with advancements in technology and economies of scale, the cost of hydrogen production is expected to decrease over time.
5.Hydrogen engines represent one of the potential solutions for decarbonizing transportation and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving hydrogen storage, infrastructure, and production methods to make hydrogen engines more viable and practical in the future.